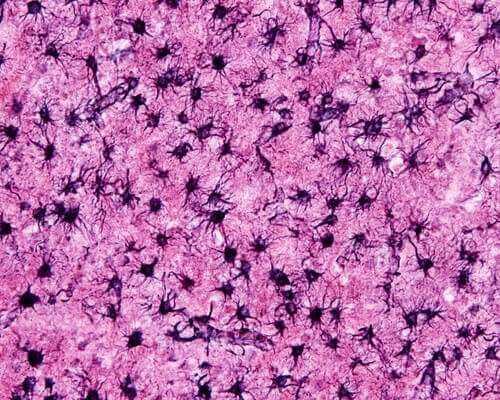
Astrocytes are part of the glial cell group. Its importance has been varying over time, at first its function was underestimated, since all the role assumed by neurons, however, it has been shown that not only do they perform a passive function, that is, their task is not simply to complement neurons.
These types of glial cells are responsible for the construction of nerve pathways, which among other functions:
- So there’s a lot to discover and know about astrocytes.
- In fact.
- It is surprising how they react to neural activity and how it is repaired and communicated.
- Let’s go further.
“As long as the brain is a mystery, the universe will remain a mystery. ” – Santiago Ramón y Cajal-
Astrocytes completely surround the capillaries of the brain and form a physical barrier between blood and neurons. They are of different types that give rise to different varieties:
Out of curiosity we mention that the term astrocytes comes from the way these cells are presented, which is similar to a star in which you can see extensions projected onto neighboring cells.
In addition, astrocytes contain a protein in the cytoskeleton called glial fibrillary acid protein (GFAP), which is the characteristic that differentiates them, since it is only found in this type of cell.
Astrocytes build the information transmission pathways in our brains and, thanks to the neural connections they provide, are responsible for helping guide the journey that axons make, through molecules that attract or grow back.
As good builders, are astrocytes aware of what is happening, in real time?Nervous function. Therefore, they are responsible for maintaining the balance of neurons or cerebral homeostasis, so they act as a metabolic medium, which is achieved by maintaining the ion balance of nerve cells.
In addition, they participate in the maturation, training and maintenance of neural synapses. Thanks to astrocytes, neurons receive oxygen, nutrients and protective isolation.
Now, through a process called phagocytosis, these cells are able to remove waste from brain metabolism, a process that is beneficial because it allows the disposal of waste and pathogens and is transported transporting waste to the blood so that it can be disposed of. In addition, when brain damage occurs, the astrocytes move to the site of the injury to remove dead neurons.
On the other hand, they are part of the important blood brain barrier (BEM), so they are intermediate between the circulatory system and neurons as a filtering mechanism, so they are also responsible for regulating the passage of molecules from the blood to the brain.
Astrocytes are linked to neurotransmitters because they actively respond to them and have receptors for binding, it is a true method of communication of this type of glial cells that is complemented by another way of sending messages, ingilising the space in the synaptic junctions and acting as a signal. modulators between neurons.
There is a pathological process by which the number of astrocytes increases rapidly and disproportionately; this process is the one that accompanies inflammatory phenomena and is called reactive gliosis.
There are two types of astrocytes when this type of proliferation occurs: A2, which has restorative functions, and A1, which promotes the degradation of nerve tissue.
Reactive gliosis occurs when there is damage to the nervous system and is followed by a proliferation of these cells in areas that have suffered damage, a phenomenon that has been reflected in many studies.
Reactive gliosis is beneficial because it causes a synthesis of neurotrophic factors responsible for promoting the survival of neurons, on the contrary, it is harmful because it generates a glial scar, which represents a barrier to axonal growth.
This phenomenon is vital in clinical research, as it is a great hope for new therapeutic models, for example, stem cell transplants are studied using neurotrophic factors that promote neuronal regeneration, in fact, they are being investigated to treat neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer’s. Parkinson’s disease.
Astrocytes are responsible for building bridges of communication between the different cells of the nervous system, in addition, as they are responsible for isolating and eliminating harmful substances, act against brain damage and allow the restoration of these communication channels.
Astrocytes are prepared to forge links between different sites and anatomo-functional elements, such as the circulatory system and blood brain barrier, neurons between them and with brain neurotransmitters, among others, are also fantastic when it comes to keeping the nerve pathways, as they keep the nervous system in internal balance.
In view of all these discoveries, we can only hope that neuroscience, through the continuous study of these cells and their possible applications, will lead to significant advances in health related to this type of glial cell.