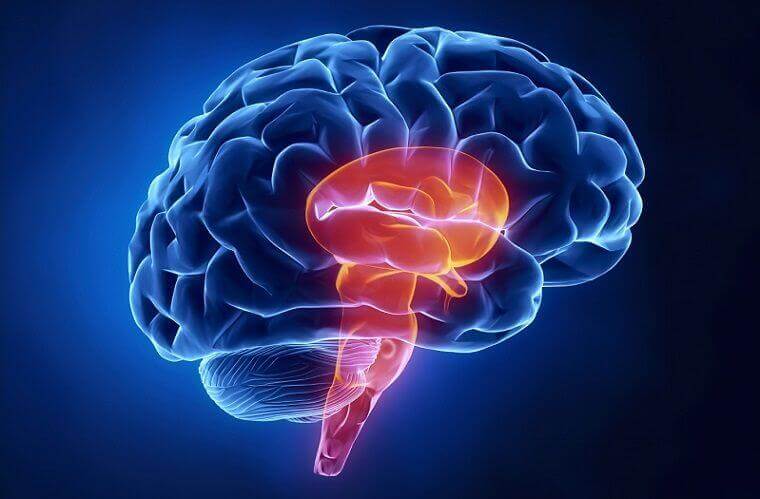
The brainstem is the tube-shaped brain structure located at the lowest position of the brain, near the spinal cord; in fact, it seems like an extension of it.
It is the part of the brain that regulates much of our autonomous or partially autonomous vital functions, such as heart rate and breathing. It is a fundamental brain structure for survival, and any injury in this part of the brain can be fatal.
- It is a vital center of our body and is divided into several areas with specific functions.
- The image of the horizontal section of the brainstem resembles the image of a butterfly.
An exceptional film, The Scuba and the Butterfly, tells the story of a man who suffers an injury to the brainstem and wakes from a coma with incarceration syndrome, as many of his functions have been damaged.
Next we will discover the importance of this brain structure
The brainstem can feel like a bridge between the spinal cord and the rest of the nervous system, but it’s much more than that. A multitude of neural fibers passing through the spinal cord are aligned with the brain stem.
It is composed mainly of grey substance and white substance; almost all cranial pairs, or cranial nerves, come from the same brainstem, so nerve impulses sent by the spinal cord must pass through the different regions of the brain stem.
Within this structure, there are areas containing islets of gray matter, the best known being the red core of the mesencephalus; other external areas contain white matter.
In addition to the well-defined areas of gray matter and white matter, there is another area in which the two substances are mixed: the laticular formation, that is, it has both control cores and very important connection areas.
It is divided into three sections or substructures: the mesencephalus, the brainstem bridge and the spinal cord, then we will see them.
The three structures that make up the brainstem are
In addition to vital functions such as consciousness, breathing, heart rate and gastric secretion control, the brainstem is involved in other important and basic functions to keep us alive, such as regulating body temperature, swallowing, vomiting, coughing and pain.
It is also the most important means of communication between the body and the brain, through it pass the adug (brain-body) and efferent (brain-body) pathways, making this structure a fundamental part of the brain for survival.
The brainstef trunk could be compared to very sophisticated engineering work. So sophisticated that any delay has devastating consequences for the rest of the body. Remember that this area is the director of many of our vital functions. A tube containing a butterfly full of life.