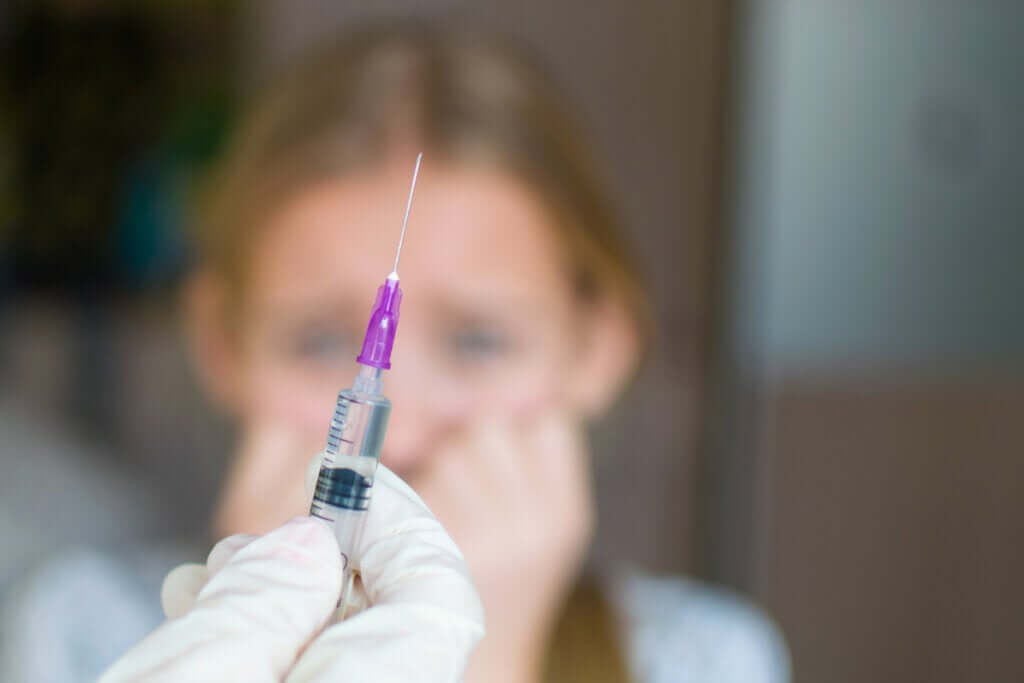
Trypanophobia or needle fear is a very common phobia that also receives other names, such as belonephobia; in fact, some authors are more accurate, calling the fear of needles belonephobia and trypanophobia the fear of injections. In this article we will use the concept of tryptophobia to refer to phobia of needles and injections.
What is this fear?What are your symptoms and possible causes?In addition to answering these questions, let’s talk about the two most effective psychological therapies to treat specific phobias like this.
- Trypanophobia is a specific type of phobia (an anxiety disorder) characterized primarily by excessive.
- Intense and irrational fear of needles and injections.
While it is true that needles can cause harm if not used properly, the reality is that in this phobia (as in all specific phobias) fear is disproportionate.
People with trypanophobia cannot collect or donate blood, get tattoos, and get vaccinated; if they succeed, they do so with great anxiety.
As you can see, one of the symptoms of phobias is that they interfere in one way or another in a person’s daily life, and the fear of needles also causes a great discomfort in those who suffer from them.
The phobic stimulus, in any particular phobia, is one that causes anxiety or intense fear, in the case of trypanophobia the object that scares are needles, but also syringes or the possibility of receiving a vaccine, in addition, it is important to note that in some cases the individual is afraid of elements related to needles or syringes, such as the smell of the hospital , stretchers and surgical equipment, among others.
According to the DSM-5 (2014) (Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders) criteria, the symptoms of trypanfobie are:
Symptoms of this phobia can also be clarified by grouping them into three categories:
When do symptoms appear? Basically, when a person thinks, visualizes, or touches needles, this can also happen when they go to the doctor or dentist, ultimately the symptoms appear every time a person goes through a needle-related situation.
Depending on the intensity of the phobia, symptoms may or may not appear in certain situations, for example, for some people, it is enough to think about the needles for symptoms to appear, on the other hand, other people need to be in real contact with the needle for this to happen.
There are several causes that can explain trypananophobia or fear of needles. One of the most common causes is a traumatic needle-related experience, such as getting injured when drawing blood, for example.
It is even possible to explain this through associative learning (classic conditioning), where the mind ends up associating a stimulus with a negative response. One of the key figures in this type of learning was the American psychologist John Watson. caused a boy named Albert to have a phobia of white mice.
However, like any phobia, trypanophobia can also be acquired by vicar conditioning. For example, having a parent who has trypanophobia and see how much it affects you. Finally, some authors claim that humans are biologically?Programmed? (or predisposed) to develop certain types of phobias, especially those that enabled our ancestors to survive.
According to these theories, we have developed certain phobias to manifest the response of struggle or flight, which would save us as a species; even fears are dormant in very primitive areas of the brain.
According to clinical psychology, the Guide to Effective Psychological Treatments of Pérez et al. (2010) and according to Horse (2002), the two treatments par excellence (the most effective) to treat specific phobias are:
In this type of treatment, the therapist gradually exposes the patient to thephobic stimulus.
In the case of fear of needles, the person would be exposed to the phobic object in question first to think about the needles, then to view images and videos, etc. , to be able to approach them, touch them and even receive an injection, for example. The ultimate goal is for the person to deal with the situation without anxiety.
Cognitive therapy, specifically cognitive restructuring, aims to alter the irrational and catastrophic thoughts presented by the patient in relation to their phobia. In the case of fear of needles, these thoughts may be, for example, “Can’t I stand needle pain?”or will it hurt?. It’s about replacing these thoughts with more realistic and functional ones.
Fear of needles is often associated with other phobias, such as hematofbia (fear of blood) or aphimophobia (fear of sharp objects), that is, if you have trypananophobia, these other fears are also likely to appear, because association or generalization is very simple.
In the case of hematophagia or acmophobia, the psychological treatments used will be the same as for tryptophobia, but adapted to this particular phobia.
On the other hand, although cognitive therapy and exposure therapy have proven to be the most effective therapies for this type of disorder, there are other alternatives that can also help combat phobias, such as psychoeducation, mindfulness and cognitive behavioral therapy, among others.
Remember that if you feel that your phobia interferes with your daily life, the best option is to call a professional specialized in the topic (preferably a clinical psychologist).
“Nothing in life should be feared, only understood. ” – Marie Curie-