Cerebrovascular diseases are the most common cause of neurological problems, they are responsible for 50% of all problems and the third leading cause of death worldwide, behind heart disease and cancer, one of these diseases is stroke, also known by their acronym or stroke.
These abnormalities in brain function are caused by pathological processes in blood vessels and usually lead to neurological changes. The brain depends on the blood supply, so when there is a blockage or rupture of the veins and a region has its blood flow interrupted for a while. Within a few minutes neural damage occurs, if the situation persists we reach the point of death of neurons with irreparable damage and irreversible symptoms.
- One possible procedure is detection through x-ray exams performed by doctors and neurologists.
- For example.
- A CT scan or MRI can provide a lot of information about the brain structures affected by a stroke.
In addition, it is also important for a psychologist to conduct neurological research, so evidence that is not always detected by radiological examinations, such as behavioral changes, can be observed, both procedures are necessary for a more complete and accurate diagnosis.
This type of cerebrovascular pathology is formed by a heterogeneous group of disorders in which brain damage occurs due to a vascular problem, whose prevalence has increased in recent decades due to greater accuracy in the detection of cases using neuroimaging techniques. it also contributes to this increase.
The main risk factors are those that facilitate the process of fat accumulation in blood vessels, calcification or loss of flexibility, i. e. high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes and smoking, are more common in people over 60 years of age. Stroke causes disruption of blood flow to a part of the brain, causing a lack of oxygen that, if maintained for a while, causes injury to the affected area or surrounding areas due to the death of brain tissue.
Stroke symptoms are often indoloal and transient, so they are often not diagnosed. There is no pain because the brain has no pain receptors and can be transient because blood flow is restored after a brief interruption. Motor and sensory symptoms usually occur on the opposite side of the affected area in the brain. For example, if there is a decrease in blood flow to the right part of the brain, the consequences will usually be observable in the left half of the body.
In addition, strokes often cause loss of strength or numbness in the middle of the body (face, arm, leg?). There may also be sudden, partial, or total vision loss in one or both eyes. Another symptom is difficulty speaking and understanding others.
Stroke causes disruption of normal blood flow in the brain, also called a stroke, and can be caused by a venous obstruction (ischemic stroke), or by bleeding (hemorrhagic stroke). Let’s look at the characteristics of each:
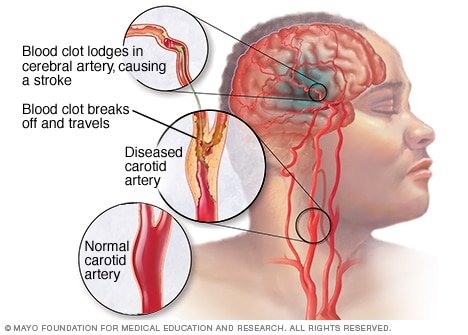
The cause of ischemic strokes is the interruption of blood flow due to a blockage in the blood vessels. A clot travels through blood vessels to the brain and gets stuck somewhere in an artery, causing a blockage. The region irrigated by this vein stops receiving blood and therefore also stops receiving oxygen, which damages the non-irrigated region.
The causes of this type of stroke are lack of systemic irrigation, thrombosis or embolism.
What sets this stroke apart from the previous one is the high mortality rate compared to ischemic stroke, the mortality rate of patients with this disease is approximately 30-50% in the first month after the onset of bleeding.
Severity is greater in this type because spilled blood also causes damage, i. e. bleeding alone is another damage factor added to the lack of irrigation that can occur in the neighboring area, the cause of a stroke is the rupture of a weak venous wall The mechanisms behind this rupture of the vessels are mainly two : aneurysms and hypertension.
The prevalence of stroke today is around 3. 5% for the population over the age of 64, between the age of 64 and 74 there are more cases among men, but from the age of 75, however, the prevalence increases considerably among women.